Last week I released v0.4.1 of ProbABEL, just a few days after releasing v0.4.0, which contained a small, but irritating bug.
This release took quite some time to create, but features quite a few bug fixes, including a major one: for the first time since the filevector format was introduced somewhere in 2009/2010, the Cox proportional hazards regression module works with filevector/DatABEL files. This is a major step forward, because up till now we had to maintain two branches of code: trunk, with all the regular updates and improvements, and the old branch that contained the Cox PH module that was only capable of reading text files.
Another notable change is the incorporation of 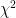 values in the output files. At the moment these are based on the LRT (likelihood ratio test), except where that doesn’t make sense (e.g. when using the
values in the output files. At the moment these are based on the LRT (likelihood ratio test), except where that doesn’t make sense (e.g. when using the --mmscore option. The implementation was relatively easy, because part of the code was still there from previous versions; it was disabled however, because it didn’t deal with missing genotype data. Now it does. Using the LRT is also easier in the case of the 2df (or genotypic) genetic model, where using the Wald test is not straightforward.
The third user-visible change was a change in the [code]probabel.pl[/code] script that hides some of the details (e.g. the location of the files with genotype data) of running a regression for the user. Previously, using the -o option meant that the output file name was constructed from the name of the phenotype file, the argument of the -o option and a fixed extension that depends on the model(s) being run. Starting with v.0.4.0 this behaviour has changed. If the -o option is specified its argument is used as the start of the output file name, with only the fixed extension appended to it. This allows users to specify output in a different directory than the one where the phenotype file was created.
Packages for Ubuntu Linux (or one of its derivatives and probably also Debian) can be found in the GenABEL PPA (personal package archive). Previously we also released pre-compiled Windows binaries, but I’ve stopped doing that. They were never tested anyway, and I think there isn’t much demand for them anyway. Most people who do genome-wide association studies use Linux servers anyway.
Development of ProbABEL (and other members of the GenABEL suite) takes place on this R-forge page. If you are in search of an open source project to contribute to, feel free to contact us!
User support for the GenABEL suite can be found at our forum.
Related Images: